
R513A refrigerant is a new way to cool things. It helps the environment while keeping things cold. It mixes HFO-1234yf and HFC-134a for good results. This refrigerant does not harm the ozone layer. It also has a small effect on global warming. Many industries now want greener options. R513A is a great choice to replace R134a in cooling systems. It works well with current equipment, making it easy and eco-friendly to use.
Key Takeaways
- R513A is a refrigerant that is safe for the ozone. It also has low global warming effects, making it eco-friendly for cooling systems.
- Switching from R134a to R513A is simple and affordable. Most systems need only small changes, saving both time and money.
- R513A works with current equipment and uses the same oils as R134a. This means no big upgrades or changes are needed.
- Using R513A lowers greenhouse gases, helping the planet while keeping cooling systems efficient.
- R513A is safe to use. It is not flammable or toxic, making it safe for users and technicians.
Characteristics of R513A
Thermodynamic Properties
R513A has great thermodynamic properties, making it very reliable. It works well in many temperatures, ensuring steady and efficient cooling. Tests show R513A performs like R134a in key areas. These include the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and volumetric capacity.
| Metric | R134a Performance | R513A Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Performance (COP) | Similar | Similar |
| Volumetric Capacity | Similar | Similar |
Studies also highlight its heat transfer abilities. For example, tests on flow boiling in small tubes show its stable performance.
| Experiment Title | Focus |
|---|---|
| Numerical simulation on flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of R513A in the horizontal microfin tubes | Shows R513A’s thermodynamic behavior |
These features make R513A a solid choice for cooling. It works well in homes and large industries.
Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP)
R513A has an ozone depletion potential (ODP) of zero. This means it does not damage the ozone layer. Older refrigerants harmed the ozone, but R513A is safer. Choosing R513A helps protect the atmosphere while keeping things cool.
Global Warming Potential (GWP)
R513A stands out for its low global warming potential (GWP). R134a has a GWP of 1300, but R513A is much lower. Switching to R513A can cut emissions by up to 27.7% in some places.
| Refrigerant | GWP Value | Performance Metrics | Life Cycle Emission Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| R134a | 1300 | Baseline | N/A |
| R513A | Low | Matches R134a | 8.4–16.7% in China, 14.7–27.7% in South Korea |
| R515A | Low | Needs bigger compressor | N/A |
| R1234ze(E) | Low | Few changes needed | N/A |
Using R513A helps the planet without losing performance. Its low GWP makes it perfect for cutting carbon footprints.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
A great thing about R513A is how easily it works with current cooling systems. If you want to switch to this refrigerant, it fits well with equipment made for R134a. This makes changing over simple and saves money.
Drop-In Replacement for R134a
R513A can replace R134a in many systems without big changes. You don’t need to upgrade parts like compressors, condensers, or evaporators. This means less downtime and an easy switch.
Tip: Talk to a trained technician before switching to R513A. They can check your system and make sure it runs efficiently.
Lubricant Compatibility
R513A works with the same oils used in R134a systems, like POE oils. You won’t need to replace or clean out the lubricant. This saves time and keeps your system safe from damage.
Minimal Adjustments Required
Most systems only need small changes to work well with R513A. For example, you might adjust the expansion valve to match the refrigerant’s properties. These small fixes help your system run its best.
Long-Term Reliability
Switching to R513A won’t hurt your system’s reliability. Its properties are very similar to R134a, so it performs just as well. Using R513A can make your system last longer and be better for the environment.
Note: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using a new refrigerant. Safe handling and proper setup are very important.
By choosing R513A, you get a green refrigerant that works with your current system. It’s a smart choice for people and businesses wanting eco-friendly cooling without spending too much.
Advantages of R513A
Environmental Benefits
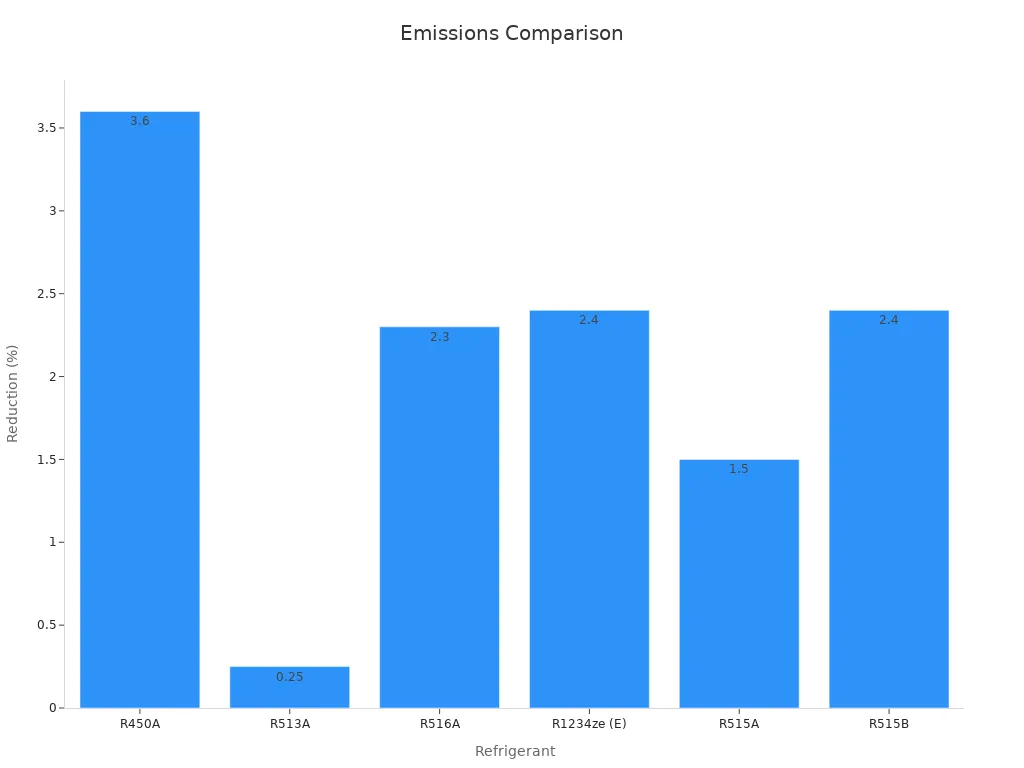
Using R513A helps lower your impact on the environment. It has a much smaller global warming potential (GWP) than older refrigerants like R134a. By choosing R513A, you help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Studies show R513A cuts emissions by 0.25% compared to R134a. This may seem small, but every effort toward sustainability counts.
| Refrigerant | Emission Reduction Compared to R134a (%) |
|---|---|
| R450A | 3.6 |
| R513A | 0.25 |
| R516A | 2.3 |
| R1234ze (E) | 2.4 |
| R515A | 1.5 |
| R515B | 2.4 |
R513A also has an ozone depletion potential (ODP) of zero. This means it does not harm the ozone layer like older refrigerants did. Choosing R513A helps protect the planet while keeping your cooling systems efficient.
Safety Features
R513A is very safe and reliable for cooling systems. It has an A1 safety rating under the ASHRAE 34 Standard. This means it is non-flammable and non-toxic. These features make it safer for both users and technicians.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-flammable | R513A has an A1, non-flammable safety rating. |
| Non-toxic | It is non-toxic, ensuring safety for everyone. |
| Reduced risk of fire | Its non-flammable nature lowers fire risks during leaks or sparks. |
| Simplified maintenance | Technicians don’t need special training to handle R513A. |
| Compliance with regulations | Meets current environmental rules without sacrificing safety. |
You can trust R513A because it reduces risks. Its non-flammable property lowers fire hazards, even during leaks. Technicians can work with it easily, without extra training. It also follows environmental rules, keeping safety and performance in balance.
Energy Efficiency
R513A is energy-efficient and helps save on electricity costs. Its properties are similar to R134a, providing steady cooling. Systems using R513A stay efficient, even in tough conditions.
Switching to R513A lowers energy use without losing cooling power. It works well for homes and businesses alike. Its efficiency reduces utility bills and cuts your carbon footprint. This makes it a smart and eco-friendly choice for everyone.
Easy Switch from R134a
Changing from R134a to R513A is simple and affordable. You don’t need to replace your current cooling systems. This refrigerant works well with equipment made for R134a, so big changes aren’t needed. Let’s see why switching is so easy.
Small System Changes
R513A is very similar to R134a, so only small fixes are needed. For example, you might adjust the expansion valve to improve performance. These tiny tweaks help your system work well with the new refrigerant.
Works with Current Parts
You won’t have to replace important parts like compressors or condensers. R513A also uses the same oils as R134a, like POE oils. This means no time wasted on oil changes or cleaning the system.
Tip: Always ask a trained technician before switching to R513A. They can check your system and make sure it works perfectly.
Real-Life Success Stories
Tests show that using R513A is easy and effective. Here are some examples:
| Study Title | Results |
|---|---|
| Experimental exergy analysis of R513A to replace R134a in a small capacity refrigeration system | Proved R513A works well in small refrigeration systems. |
| Experimental assessment of R134a and its lower GWP alternative R513A | Showed R513A performs great in many cooling systems. |
| Thermodynamic analysis of two evaporator vapor compression refrigeration system with low GWP refrigerants in automobiles | Found R513A can replace R134a with small changes, improving cooling power. |
These studies prove how easily R513A fits into current systems. It’s a great choice for homes and businesses.
Saves Time and Money
Switching to R513A is quick and saves money. Since it works with your current setup, you don’t need to buy new equipment. Small changes mean less downtime, making the switch smooth and easy.
By choosing R513A, you get a green refrigerant without a complicated upgrade. Its compatibility, proven results, and cost savings make it the best replacement for R134a.
Applications of R513A
Residential Air Conditioning
R513A is a great option for home air conditioners. It cools well and helps the environment at the same time. Companies like STULZ already use R513A in their systems. This shows it is both reliable and eco-friendly.
- STULZ uses R513A because it has a low GWP.
- Using R513A supports the EU’s F-Gas rules to cut emissions.
- STULZ leads in making air conditioners greener with R513A.
Choosing R513A for your home helps the planet without losing comfort.
Commercial Refrigeration
R513A works really well in commercial refrigerators. It cools efficiently and meets strict environmental rules. Unlike older refrigerants, R513A has a lower GWP and is safer to use.
| Refrigerant | Global Warming Potential (GWP) | Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) | Toxicity | Flammability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R513A | 56% less than R134a | Zero | Low | Non-flammable |
| R134a | Higher GWP | Harms ozone | Moderate | Flammable |
Switching to R513A makes refrigeration safer, greener, and more efficient.
Automotive Cooling Systems
R513A is also being used in car cooling systems. It works well while saving energy and cutting emissions. Places using R513A report big improvements in cooling and efficiency.
- Ice arenas using R513A saved 13-22% on energy costs.
- A facility in Ontario boosted cooling by 49% and cut power use by 13%.
R513A keeps cars cool and helps the environment. Its use in cars shows how versatile and effective it is.
Industrial Cooling Applications
Industrial cooling systems are important for keeping factories and storage areas cool. These systems often work hard and need reliable refrigerants. R513A is a great choice because it works well and helps the environment.
R513A has many benefits for industrial cooling. It has a low global warming potential (GWP), making it eco-friendly. It also saves energy, using less power even in tough conditions. Plus, it is non-flammable, so no extra safety tools are needed.
Tests show R513A performs very well in demanding cooling systems. The table below shows key benefits:
| Metric | Improvement Details |
|---|---|
| GWP Reduction | Cuts GWP by up to 70% compared to R410A. |
| Safety | Non-flammable, so no extra safety devices are needed. |
| Efficiency | Better efficiency and steady performance lower power use. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Lower setup costs and easier maintenance save money. |
Switching to R513A saves money and improves system performance. It works with current equipment, so changes are simple and downtime is short. Whether for food plants, medicine factories, or data centers, R513A is a smart and green solution.
Using R513A not only boosts cooling but also helps the planet. It’s a smart and responsible choice for industries that want to be eco-friendly.
R513A is efficient, safe, and good for the environment. It doesn’t harm the ozone and has low global warming effects. It works well with current equipment, making switching easy. R513A is great for homes, businesses, and industries. It cools reliably while helping the planet.
Using R513A supports a greener future. Its eco-friendly features help fight climate change. Choosing R513A meets your cooling needs and shows you care about Earth.
FAQ
Why is R513A good for the environment?
R513A doesn’t harm the ozone layer because it has zero ozone depletion potential (ODP). It also has a low global warming potential (GWP), which helps reduce pollution. By using R513A, you help protect the planet and cut greenhouse gases. ?
Can R513A replace R134a in cooling systems?
Yes, R513A works well in systems made for R134a. You only need small changes, so switching is easy and affordable. It even uses the same oils, saving time and effort.
Is R513A safe to use?
R513A is very safe because it’s non-flammable and non-toxic. It has an A1 safety rating, meaning it’s safe for people and technicians. Just follow safety rules when handling it.
Does R513A save energy?
Yes, R513A is energy-efficient, just like R134a. It uses less electricity while keeping cooling reliable. This makes it a smart and eco-friendly choice for homes and businesses.
Where can R513A be used?
R513A is great for home air conditioners, commercial refrigerators, car cooling systems, and industrial cooling. Its eco-friendly features make it perfect for many cooling needs.
Tip: Always ask a technician to check if your system is ready for R513A.




